Small Cell vs. Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
Erlonat Tablet 100 mg (Erlotinib) for Lung Cancer
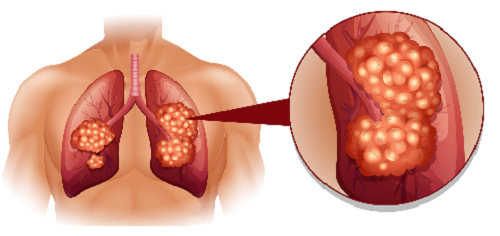
 Lung cancer is divided into two types: Small Cell and Non-Small Cell.
Lung cancer is divided into two types: Small Cell and Non-Small Cell.
Small cell lung cancer is a disorder in which malignant (cancer) cells develop in lung tissues.
Small cell lung cancer is divided into two categories. These two categories of cells contain a wide range of cell types. Each type of cancer cell grows and spreads uniquely. The many varieties of small cell lung cancer are called after the different types of cells seen in the tumor and how they appear under a microscope:
- Small cell carcinoma (oat cell cancer).
- Combined small cell carcinoma
After a diagnosis of small cell lung cancer, tests are performed to see if cancer cells have spread throughout the chest or to other areas of the body.
Small cell lung cancer is diagnosed using some of the same techniques used to stage the illness. Staging is the procedure for determining whether cancer has migrated from the chest to other body regions. MRI of the brain, CT scan, PET scan, Bone scan.
Small cell lung cancer is classified into the following stages:
- Limited-Stage Lung Cancer with Small Cells
Cancer in the limited stage has migrated to the space between the lungs or the lymph nodes above the collarbone from where it began in the lung.
- Small Cell Lung Cancer in the Advanced Stage
Cancer has gone beyond the lung, the space between the lungs, or the lymph nodes above the collarbone to other parts of the body at the widespread stage.
- After treatment, small cell lung cancer might recur (come back).
Cancer may return in the chest, central nervous system, or other body areas.
Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer
NSCLC (non–small cell lung cancer) accounts for over 85% of all lung cancers. NSCLC is classified histologically into adenocarcinoma, squamous cell carcinoma (SCC), and large cell carcinoma. Patients with NSCLC should get a comprehensive staging workup to determine the degree of their disease, as stage influences therapy options. Treatment options include surgery, chemotherapy, endoscopic stents, radiation therapy, targeted treatments, and immunotherapy.
Major differences between Small and Non-Small lung cancer:
- Under a microscope, malignant cells in a person with small cell cancer seem small and spherical whereas, non-small cell lung cancer cells are bigger.
- Small cell lung cancer is, on average, more aggressive than non-small cell lung cancer. Small cell lung cancer spreads more rapidly than non-small lung cancer.
- Small cell lung cancer symptoms and non-small cell lung cancer symptoms are similar. The symptoms include a persistent cough, hoarse throat, shortness of breath and wheezing, chest pain and discomfort, loss of appetite, swelling in the veins of the face and neck, etc. Symptoms may not develop until cancer has progressed to a later stage.
- Small cell lung cancer has 2 stages of diagnosis: the limited stage and the extensive stage. Non-small cell lung cancer has 4 stages of diagnosis: stages 1, 2, 3 and 4.
- Treatments for small cell lung cancer mainly include chemotherapy, radiation therapy, surgery. Whereas treatment for non-small cell lung cancer includes surgery, chemotherapy, immunotherapy, targeted treatments, radiation therapy, and endoscopic stents.
 Erlonat tablet 100mg is used to treat non-small cell lung cancer that has progressed to other body parts or is locally advanced. Erlonat tablet should be consumed one hour before or two hours after a meal. Diarrhea is a possible side effect.
Erlonat tablet 100mg is used to treat non-small cell lung cancer that has progressed to other body parts or is locally advanced. Erlonat tablet should be consumed one hour before or two hours after a meal. Diarrhea is a possible side effect.
Erlonat tablet (Erlotinib ), often known by the brand name Tarceva, is a type of targeted cancer medication. Erlonat tablet is used in conjunction with the chemotherapeutic drug gemcitabine to treat non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) that has spread (advanced) and advanced pancreatic cancer.




 :
:  +91 – 9999064250 | 9811604444 | 9811604424
+91 – 9999064250 | 9811604444 | 9811604424