Prostate Cancer and Enlarged Prostate – Causes, Symptoms, Prevention and Treatment
Prostate Cancer and Enlarged Prostate
Cancer that develops in the prostate glands is known as prostate cancer, and it is one of the most commonly affecting cancers in men. While some prostate cancer grows gradually and does not require any treatment, some can spread rapidly and become aggressive.
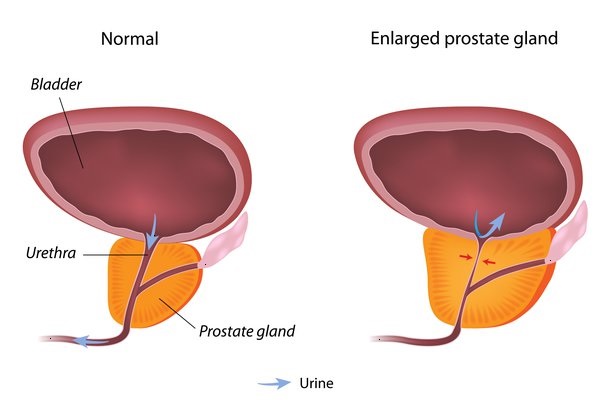
What is an enlarged prostate?
An enlarged prostate is a condition in which the prostate becomes larger in size. Enlarged prostate can be treated by changing lifestyle, taking effective medications like Enzamide 40mg Capsule, and opting for surgery.
Symptoms of Prostate cancer and enlarged prostate
Symptoms of prostate cancer are:
- Bone pain
- Blood in the urine
- Erectile dysfunction
- Weight loss
- Blood in the semen
Symptoms of enlarged prostate are:
- Urgent need to pee
- Bleeding, bladder stones, bladder damage
- Urinary tract infection
Causes
Doctors are not specific about what are the causes of prostate cancer and enlarged prostate. This type of cancer usually begins when prostate cells start developing changes in their DNA. The sudden change in the DNA of the prostate cells makes them divide and grow more rapidly than other normal healthy cells. When abnormal prostate cells accumulate, this leads to the death of healthy cells and causes the formation of a tumor in the nearby tissues. With time these abnormal states metastasize to other regions of the body.
Risk factors
The following are the risk factors for enlarged prostate or prostate cancer in men.
- Research says that men who are 50 years or above run a higher risk of prostate cancer than men who are young or less than 50 years.
- If you have obesity, you are at increased risk of prostate cancer compared to those with proper body weight. Cancer will become aggressive and is more likely to return after treatment if you have obesity.
- Black people are at a high risk of developing prostate cancer and enlarged prostate in contrast to other races. Black people also have a high-risk factor for developing advanced or aggressive prostate cancer.
Prevention
If you want to lower your risk of enlarged prostate or prostate cancer, then you must follow the following prevention and treatment methods.
- Always eat healthy foods instead of taking supplements. In order to maintain a healthy weight, you must take food that are rich in both vitamins as well as minerals. Instead of taking supplements, take good food rich in nutrients to lower your risk of an enlarged prostate or prostate cancer.
- Lifestyle and diet changes will lower your prostate cancer or enlarged prostate risk factors. Consume a lot of fruits and vegetables and limit alcohol consumption.
- Exercise daily and maintain a healthy and fit body. If you have obesity, talk to your doctor and make an effective plan for managing weight. Obese people are at increased risk of prostate cancer as well as enlarged prostate. You must exercise and eat healthy food to manage your weight.
- If you think you have a risk factor for prostate cancer and enlarged prostate, seek a doctor’s appointment immediately, assess your risk, and make an effective treatment plan. Regular screening and taking effective medications like Enzalutamide, and Enzamide 40 mg will help to control the enlargement of prostate cancer and prevent your condition from becoming more aggressive.
Treatments
The right treatment procedure for prostate cancer and enlarged prostate will depend on the following factors
- Age of the patient
- Size of prostate tumor
- Their present health status
- Symptoms or warning signs etc.
Your doctor will recommend medications like enzamide to get the best results. These medications will relax the muscles in your bladder and prostate. If changes in medications and lifestyle do not work, then your healthcare provider will suggest you go for a surgical procedure to remove the prostate cancer. Know about the enzamide 40 mg price, side effects, and benefits from your healthcare team. Treatment procedures for prostate cancer and enlarged prostate include the following
- Immunotherapy
- Targeted therapy
- Active surveillance
- Radiation therapy
- Chemotherapy
- Hormone therapy