Why Taffic Tablets and Viropil Tablets are Highly Demanded Medicines for HIV?

Table of Contents
About HIV & The Best Medication for HIV
Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) is a virus that attacks the immune system, specifically targeting CD4 cells, which are crucial in fighting off infections. It is transmitted through certain body fluids, including blood, semen, vaginal fluids, and breast milk. Unprotected sex, sharing needles, and transmission from mother to child during childbirth or breastfeeding are common modes of transmission. In this article, we will discuss about best medication for HIV.
HIV progresses in stages. The initial stage, acute HIV infection, may exhibit flu like symptoms. Without treatment, HIV can develop into the more severe stage known as AIDS (Acquired Immunodeficiency Syndrome). AIDS is characterized by a severely weakened immune system, making the body vulnerable to opportunistic infections and certain cancers.
While there is no cure for HIV, antiretroviral therapy (ART) helps control the virus, allowing those infected to lead long and healthy lives. It’s crucial to get tested regularly, practice safe sex, use clean needles, and access appropriate medical care to prevent transmission and manage the condition effectively. Education, awareness, and destigmatization are vital in combating HIV and supporting those affected.
Common Symptoms of HIV:
1. Acute Stage:
- Fever
- Fatigue
- Swollen lymph nodes
- Sore throat
- Rash
- Muscle aches and joint pain
2. Chronic Stage (without treatment):
- Persistent fever
- Night sweats
- Fatigue
- Rapid weight loss
- Diarrhea
- Prolonged swelling of lymph nodes
3. Advanced Stage (AIDS):
- Severe and frequent infections (opportunistic infections)
- Persistent coughing and shortness of breath
- Recurring fever, chills, and sweats
- Rapid weight loss
- Extreme fatigue
- Memory loss, neurological disorders
It’s important to note that symptoms can vary widely among individuals, and some may not experience any symptoms for years despite being infected. Testing is the only way to confirm HIV infection accurately. If you suspect you’ve been exposed to HIV or are experiencing symptoms, it’s crucial to seek medical advice and get tested promptly. Early detection and treatment significantly improve outcomes and quality of life for those living with HIV.
What is the Best Medication for HIV?
Taffic Tablet Uses, Benefits and Side Effects:
Taffic Tablet is a combination medication used to manage HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) infection, boosting the immune system against AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome). Comprising Bictegravir, Emtricitabine, and Tenofovir Alafenamide, it curbs HIV growth, reducing complications and improving an individual’s lifespan. Taking it consistently at the same time daily maximizes its effectiveness. Missing doses may hinder recovery, so completing the full course as directed is crucial.
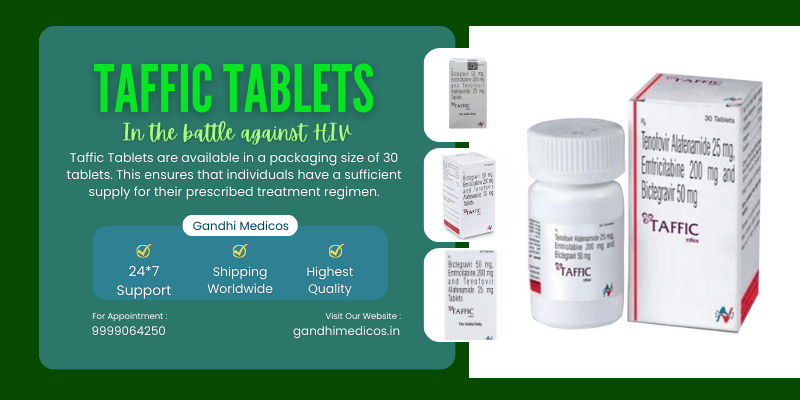
Common side effects include nausea, diarrhea, and headaches, which usually diminish over time. However, persistent or severe symptoms should be reported to a doctor. This medication might induce lethargy or weakness, advising caution while driving. Staying hydrated can help manage side effects.
Consult a doctor before starting Taffic Tablet, especially if pregnant, breastfeeding, or with any health conditions. Regular blood tests may be recommended to monitor health parameters and drug interactions.
Taffic Tablet doesn’t cure HIV/AIDS or prevent infection after exposure. It’s essential to follow the prescribed regimen alongside other antiretroviral medications. Adhering to the dosage and schedule significantly enhances its efficacy and minimizes the chance of HIV resistance. Using this medicine doesn’t prevent HIV transmission to others.
The medicine operates by inhibiting HIV replication through different mechanisms. Bictegravir prevents replication, while Emtricitabine and Tenofovir Alafenamide hinder viral enzyme action and DNA synthesis.
Warnings include interactions with alcohol, caution during pregnancy due to possible fetal harm, and its likely passage into breast milk, posing risks to the baby during breastfeeding. It may also affect alertness and isn’t advisable for driving. Patients with severe kidney or liver issues should use it cautiously, requiring dosage adjustments.In case of a missed dose, take it promptly unless close to the next scheduled dose.
Viropil Tablet Uses, Benefits and Side Effects:
Viropil Tablet is a blend of antiretroviral medications utilized in treating HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) infection, fortifying the immune system against AIDS (acquired immunodeficiency syndrome). It impedes HIV growth, lessening related complications and extending an individual’s lifespan. This medication can be taken with or without food, but adherence to a consistent schedule enhances its effectiveness. Skipping doses can hamper recovery, so completing the entire treatment course is essential unless advised otherwise by your doctor.
Common side effects encompass headaches, nasal congestion, diarrhea, nausea, weakness, fatigue, cough, and rash. While these are usually transient, persistent or severe symptoms should be reported to a doctor. Viropil Tablet might induce lethargy, recommending caution while driving. Maintaining hydration helps manage side effects.
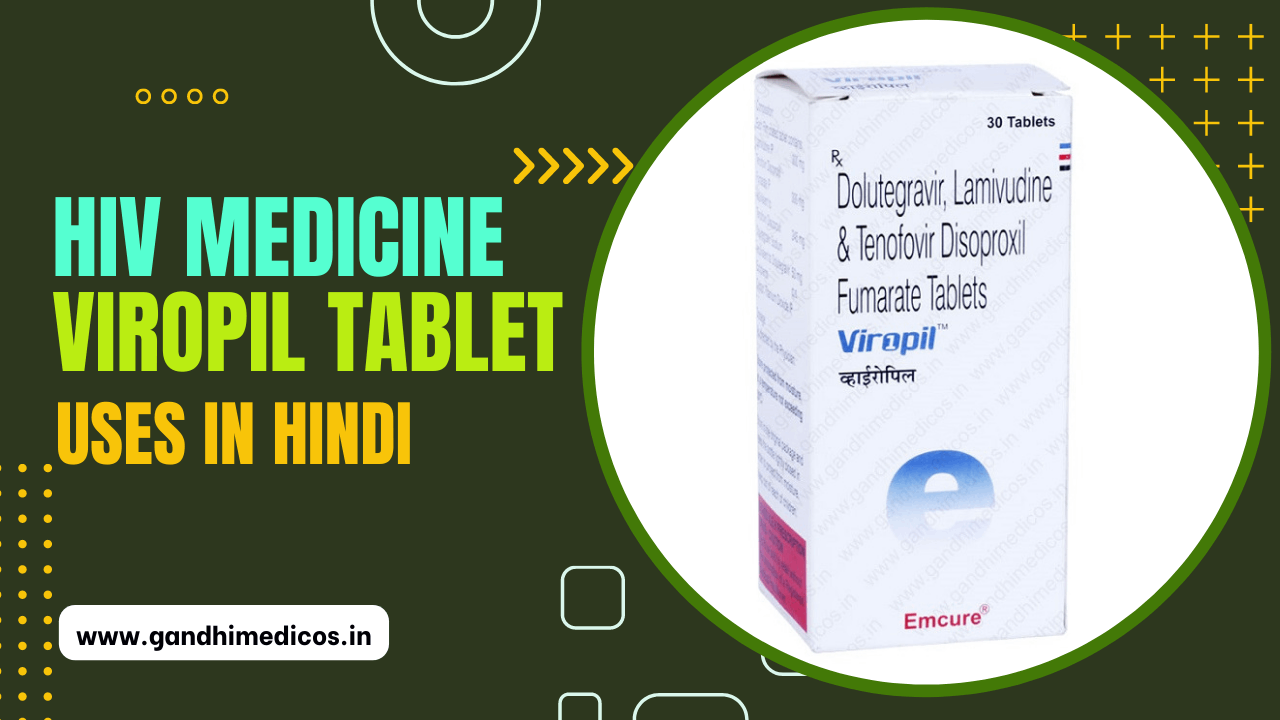
Consult your doctor before starting treatment, especially if pregnant, breastfeeding, or with any underlying health conditions. Regular blood tests might be suggested to monitor health parameters. If HIV positive, avoiding breastfeeding and sharing personal items like razors or toothbrushes is advised to prevent transmission. Seek guidance on safe sex methods to prevent HIV transmission during intercourse.
Viropil Tablet curbs HIV multiplication, enhancing the immune system’s functionality. It’s not a cure for HIV/AIDS, nor does it prevent transmission after accidental exposure to risk. Proper adherence to prescribed dosages and timing maximizes its efficacy and reduces the likelihood of HIV developing resistance to antiretroviral medications.
This medication operates by inhibiting the action of the reverse transcriptase enzyme responsible for HIV production.
Warnings include interactions with alcohol, caution during pregnancy due to fetal risks, uncertain guidance regarding breastfeeding while using this medicine, and unknown effects on driving ability. Patients with severe kidney or liver conditions should use it cautiously, necessitating dosage adjustments.
In case of a missed dose, take it as soon as possible unless it’s close to the next scheduled dose. Don’t take double doses to compensate for a missed one.


 Anti Cancer Drugs
Anti Cancer Drugs Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C Meds for HIV
Meds for HIV Ayurvedic Medicine
Ayurvedic Medicine Transplant Medicine
Transplant Medicine Respiratory System
Respiratory System +91-9999064250 / 9811604424 / 9811604444
+91-9999064250 / 9811604424 / 9811604444
 8(800)100-47-90
8(800)100-47-90
