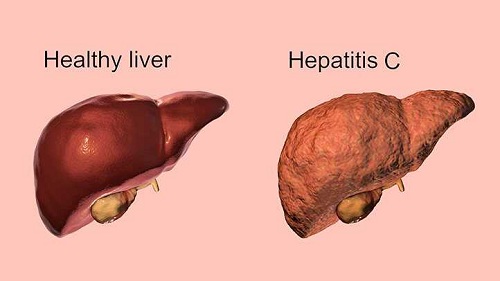
What is Hepatitis C, and what are the common Symptoms?
Hepatitis C develops from the hepatitis C virus. On entering the body, the virus attacks the liver, which leads to inflammation and infection. The other types of hepatitis, A, and B, have vaccines, but hepatitis C does not have any vaccine. Though researchers and doctors are trying their best to develop one. And because there is no vaccine, this condition is quite contagious.
There are two phases of this condition acute and chronic hepatitis C. When it comes to showing symptoms, acute hepatitis C shows symptoms quite early, whereas chronic hepatitis C symptoms take time to develop. The symptoms of chronic, are sometimes not even identifiable at first.
Research and surveys show that most hepatitis C patients don’t even show any symptoms, but the rest do face some symptoms.
The symptoms are as follows:
– Dark urine
– Abdominal discomfort or pain
– Fever
– Joint pain
– Loss of appetite
– Jaundice
These symptoms usually take 6 to 7 weeks to fully develop and become apparent.
Transmissibility
Hepatitis C is a contagious disease that spreads through blood-to-blood contact. It is not transmissible through any casual contact. But even if it is contagious, since blood-to-blood contact is the only way of transmission, it is not that contagious compared to other infections and viruses.
The transmission of the virus can take place through one of these situations:
– Sharing needles
– Sharing razors or toothbrushes
– Blood transfusion
– Since the birth (mother had hepatitis C during pregnancy)
– Organ transplant
Hepatitis C tests
Hepatitis C cannot be identified only through symptoms. Doctors will also like to know if there was any exposure to hepatitis C through any of the situations mentioned above. To check if the virus or any infection is present in the body, the doctor will do some blood tests. These tests will tell the genotype and the amount of the virus present in the blood. Such information will help in determining the medical treatment that will be most effective for the patient.
Apart from these, some more liver-related tests will be done to check if there is any liver damage and if there is any sign of excessive toxins in the blood due to failure in the liver’s functioning.
Treatment
Many patients with hepatitis C do not require medical assistance, as their immune system is capable enough to fight the injection until it clears off. In such situations, the doctors will do regular checkups to ensure that the liver is functioning properly.
Other than this, for people whose immune system is unable to fight the infection, medications are given based on the virus’s genotype. Ledikast is one such medication containing antiviral agents that effectively fight off the hepatitis C virus and the infection.