Hepatitis B Guide: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment Options

Hepatitis B Virus
Hepatitis is liver inflammation, and the hepatitis B virus leads to hepatitis B. The virus spreads when a person comes in contact with infected blood. Following are the ways which can transmit hepatitis B
- Tattooing or piercing with contaminated equipment
- Sharing needles with intravenous users of the drug
- Coming in direct contact with an infected person’s blood
- Having unprotected sexual intercourse with an infected individual
- Sharing personal items like razors with an infected individual
- Childbirth/ pregnancy when the virus gets passed on to the newborn from the mother.
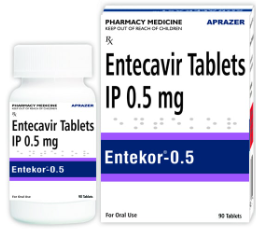
Hepatitis B virus can lead to either temporary infection or chronic long-term hepatitis. People infected with the hepatitis B virus may not notice any symptoms initially. The risk of hepatitis B virus can be dramatically reduced by Immunizing with the hepatitis B vaccine and effective medicine like Entekor 0.5 mg.
Infected people developing symptoms due to initial viral infection can have acute hepatitis, and many of them get cleared of this virus from their blood and liver. However, a minority of them who develops long-term infection suffer from chronic hepatitis B. In the case of chronic hepatitis B, symptoms disappear but later come back. Such people having chronic hepatitis B have the risk of passing the virus to others and remaining infectious. Some people don’t develop any disease symptoms and cannot get rid of this infection from their bodies. They are known as carriers and may pass this infection to others.
Symptoms of hepatitis B
Acute hepatitis B
Acute hepatitis B symptoms include the following
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite
- Fever
- Itching
- Vomiting
- Abdominal pain
- Headache
- Sleep disturbance
- Nausea
Chronic hepatitis B
These signs and symptoms can be followed by a disease named jaundice, in which the affected person observes yellowing of skin, eyes, and darkening of urine. Most people recover from acute hepatitis. But one out of ten adults may get chronic hepatitis in which people remain infected by the virus and develop chronic liver disease, so there remains a risk to pass the virus to others. Following are the symptoms of chronic hepatitis-
- Aching joints
- Fatigue
- Ill feeling
- Jaundice
- Low appetite
A minority of people with chronic hepatitis can also get liver cirrhosis, a scarring of the liver that causes poor functionality of the liver. Such people can have symptoms of serious and advanced liver infection along with the following symptoms-
- Swelling in legs
- Jaundice
- Accumulation of fluid inside the abdomen
- Gastrointestinal bleeding
People having hepatitis B and developing liver cirrhosis have a great risk of developing liver cancer.
Diagnosis
Blood tests help confirm the diagnosis of hepatitis B. Performing these tests helps detect hepatitis B in the bloodstream. The blood tests detect antibodies which are proteins produced by the immune system to attack the hepatitis B virus. People mostly recover from acute hepatitis infection within three months.
Treatment
There isn’t any permanent cure/treatment for acute hepatitis B. Treatment helps to reduce the level of virus present in the body and eases inflammation which causes hepatitis B symptoms. A small number of people with acute hepatitis B need hospitalization and develop liver failure, leading to liver transplants and even death. Doctors use antiviral medicines to treat chronic hepatitis B. Some antiviral drugs like entecavir are highly effective in treating chronic hepatitis B and entecavir 0.5 mg uses are wide to reduce the viral load in blood. Entecavir 0.5 mg price may differ based on different brands.


 Anti Cancer Drugs
Anti Cancer Drugs Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C Meds for HIV
Meds for HIV Ayurvedic Medicine
Ayurvedic Medicine Transplant Medicine
Transplant Medicine Respiratory System
Respiratory System +91-9811604444/ 9811604424/ 9999064250
+91-9811604444/ 9811604424/ 9999064250  8(800)100-47-90
8(800)100-47-90

