Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: Dissecting the Mystery
Nintedanib Capsules 100mg for IPF
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis (IPF) is a serious lung disease that causes inflammation or scarring of the lung tissues. These wounds (fibrosis) build up in the lungs over time and can affect the respiratory system. IPF is a very rare disease of the lungs, and the progression of the disease can be life-threatening.
Causes and Risk Factors
The cause of Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis remains unknown, but several risk factors can lead to acquiring the disease.
- Age– IPF is most common in adults between 50 and 70.
- Radiation exposure- Therapies used for cancer treatment can lead to higher exposure to radiation, which can cause damage to lung tissues.
- Impact on other medical conditions- Pulmonary Fibrosis may also occur in patients diagnosed with a certain kind of autoimmune disease or viral infection.
Signs and Symptoms
Chronic Coughing is the first sign that patients with IPF mostly suffer. During the last stages, patients may experience some serious symptoms, which may include-
- Chest pain
- Difficulty in breathing
- Fatigue
- Loss of appetite
- Swelling of the leg
- Joint and muscle pain
- Weight loss
Prognosis
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis is a progressive disease that can get worse over time. The cause of the disease has not been found, so patients with IPF show no serious symptoms, which becomes difficult to identify the disease. Generally, dry cough or shortness of breath indicates the presence of IPF; however, these symptoms are also common in patients with other respiratory diseases such as Pneumonia, bronchitis, and asthma. In addition, the progression of IPF is hard to tell; hence, the disease’s severity depends on the stages.
- Stage 1- Usually, patients with Stage 1 of IPF do not show any symptoms. However, they may develop dry cough or shortness of breath.
- Stage 2- In stage 2 of IPF, dry cough or shortness of breath may seem to progress.
- Stage 3- In this stage, the patient’s oxygen level can go down, and they may need oxygen 24/7.
- Stage 4- This is the final stage of IPF, in which patients may require additional oxygen support.
Diagnosis and tests
A doctor or healthcare professional may suggest some of the following tests to look out for a patient who has symptoms of IPF.
- Chest X-Ray- This is the most common type of test that a doctor may recommend to their patients to check the scars of the tissues in the lungs.
- Breathing Test- A spirometer, a medical device, is highly used to measure the functioning of the lungs. The patient takes a deep breath and blows in the tube attached to Spirometer.
- Blood Test- A doctor may take a blood test to check the patient’s oxygen and carbon dioxide levels. But unlike regular blood tests, this blood test does not use blood samples from veins. Instead, the blood sample is taken from an artery in your wrist.
- Lung Biopsy- Lung Biopsy is suggested to the suspected patients only if they fail to diagnose IPF with the above tests. The biopsy procedure is invasive. Doctors remove a tiny amount of lung tissue to evaluate the disease in the lungs.
Treatment
Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis is not curable. However, some treatments may help to slow down the progression of the disease, such as
- Oxygen therapy
- Lung transplant
- Pulmonary rehabilitation
- Medications
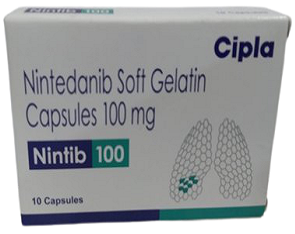
Nintedanib capsules 100mg for Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis
Nintib-100(Nintedanib capsules 100mg) is an oral capsule from the Kinase tyrosine inhibitor drug, which is highly used as a medication for patients with Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis. The capsule works by blocking the enzymes affecting the lung tissues. Nintedanib capsules 100mg are combined with docetaxel to treat metastatic lung cancer and other lung disorders. Although Nintib capsules (Nintedanib capsules 100mg) are effective when taken as per a doctor’s advice, some side effects may still occur during the initial days of Nintedanib capsules 100mg medication which may include-
- High blood pressure
- Abdominal pain
- Nausea
- Diarrhea
- Loss of appetite
However, these symptoms are temporary and will disappear within some days. If the symptoms show up for a prolonged period, it is advised to see a doctor and discontinue the medication immediately.


 Anti Cancer Drugs
Anti Cancer Drugs Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C Meds for HIV
Meds for HIV Ayurvedic Medicine
Ayurvedic Medicine Transplant Medicine
Transplant Medicine Respiratory System
Respiratory System +91-9999064250 / 9811604424 / 9811604444
+91-9999064250 / 9811604424 / 9811604444
 8(800)100-47-90
8(800)100-47-90




