What are the Symptoms and Causes of Ovarian Cancer

Ovarian Cancer: Treatment, Medicine, Symptoms and Causes
The development of cancerous cells in the female glands called ovaries is known as ovarian cancer. The cells can get rid of healthy biological tissue and reproduce at a fast pace. Two ovaries make up the female reproductive system and are found near the uterus, one on each side. The hormones progesterone and estrogen are also produced by the ovaries, which are vital hormones for the female body. Ovarian cancer comes in a variety of forms. Epithelial cancer is the most prevalent variety. It starts in the ovary’s protective cells.
The ovaries can get infected with two related kinds of epithelial cancer: The first is primary peritoneal cancer, which develops in the material lining the peritoneum; and the other one is fallopian tube cancer, which occurs in the membrane lining a fallopian tube. The tissue lining the abdomen’s organs is called the peritoneum. The treatments for these 2 cancers are the same as those for ovarian cancer. Thus, certain medical professionals also regard those two forms as ovarian cancer. Malignant germ cell tumours and stromal tumours are two other, less common kinds of ovarian cancer.
Causes
Even though there are many risk factors that can lead to the development of this disease in individuals, the cause of ovarian cancer remains unknown, like many other cancers. Based on current knowledge of health professionals, ovarian cancer begins when cells inside or near the ovaries face a mutation in their DNA. DNA is found inside all the cells, providing them with specific instructions. These changes make the cells go through a process of multiplication, resulting in the creation of tumors. Unlike healthy cells, cancer cells have the ability to last for a longer period. Besides that, they also have the capability to metastasize to other body parts.
Symptoms
There may be no early warning signs or symptoms of ovarian cancer. The disease is often advanced when you finally have any indications or symptoms. The indications and signs may include abdominal or pelvic pain, swelling, or a sense of pressure; frequent urination; difficulty eating or feeling full, a lump in the pelvic region, and digestive issues, including gas, indigestion, or constipation.
Treatment
 The most typical ways for treating ovarian cancer are surgical excision of the tumor or medication therapies, just like the treatment for any other cancer. The sort of ovarian cancer, its phase, and any unique circumstances are typically taken into account while creating treatment strategies. Since they can access cancer cells practically anywhere in the body, medications taken to cure ovarian cancer are referred to be systemic therapy. They can be administered orally or straight into the blood. Examples include chemotherapy, hormone therapy, or targeted medication therapy.
The most typical ways for treating ovarian cancer are surgical excision of the tumor or medication therapies, just like the treatment for any other cancer. The sort of ovarian cancer, its phase, and any unique circumstances are typically taken into account while creating treatment strategies. Since they can access cancer cells practically anywhere in the body, medications taken to cure ovarian cancer are referred to be systemic therapy. They can be administered orally or straight into the blood. Examples include chemotherapy, hormone therapy, or targeted medication therapy.
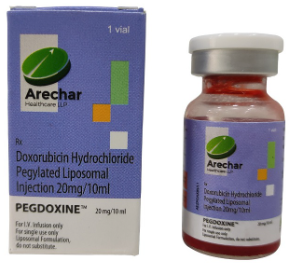
Pegdoxine is a treatment for ovarian cancer in females. This drug is a member of the anthracycline class of antineoplastics, which are drugs used to treat cancer. This drug contains Doxorubicin pegylated liposomal as its main ingredient. Arechar produces it, and it comes in vial form. By complexation between DNA base pairs and generating steric blockages, this injection prevents the synthesis of DNA and RNA.
It also stops topoisomerase-II at the site of DNA cleavage. Doxorubicin is also a potent iron chelator, and its pegylated formulation shields the liposomes to lengthen the duration that blood circulates. A doxorubicin formulation known as pegylated liposomal doxorubicin places the drug’s actual molecule inside a polyethylene glycol-coated liposome comprised of a variety of lipids. A qualified healthcare provider should only administer this injection because it may interact with some other medications and increase the risk of side effects.


 Anti Cancer Drugs
Anti Cancer Drugs Hepatitis C
Hepatitis C Meds for HIV
Meds for HIV Ayurvedic Medicine
Ayurvedic Medicine Transplant Medicine
Transplant Medicine Respiratory System
Respiratory System +91-9999064250 / 9811604424 / 9811604444
+91-9999064250 / 9811604424 / 9811604444
 8(800)100-47-90
8(800)100-47-90
